Table of Contents:-
- Meaning of Media
- Definition of Media
- Characteristics of Media
- Types of Media
- Role of Media in Disaster Management
- Why Media Covers Disaster News?
- Relationship between Media and Society
Meaning of Media
The term ‘media’ refers to various communication channels and platforms used to distribute information, news, entertainment, and advertising, like radio, newspapers, television, magazines, etc. A lot of diverse functions are performed by these communication channels, including presenting the ad messages, conveying information and news, offering entertainment which could appeal to a specific or a large set of people, etc. The communication messages of the advertisers are carried by the media to the audience. Hence, they act as a link between the consumer and the sellers of goods and services.
Media is defined as impersonal means of communication by which written, visual auditory or sometimes a combination of such messages are transmitted directly to the audiences. In simpler terms, the term media denotes the means of communication with a large number of people spread over cities, communities or countries through written or printed word voice and sound or visual images or a combination of these.
In simple terms, media is an organised means of reaching a large number of people, quickly, effectively and efficiently.
The two main characteristics of media are as follows:
i) It can reach millions of people in a short time; even instantaneously.
ii) Audio media transcends the limits of illiteracy and visual media can be effective in a multilingual society as well.
iii) It is cost-effective and generally user-friendly.
iv) Generally, media provide one-way communication i.e., to the receiving people.
Television, radio, newspapers, magazines, audio and video as well as movies are examples of media. These are useful in India’s multilingual, traditional, and largely illiterate society.
Definition of Media
According to George E. Belch, “Media refers to non-personal channels of communication that carry the message without interpersonal contact between sender and receiver”.
According to Philip Kotler, “The communication channels through which message moves from sender to receiver is called media”.
It refers to the various channels through which an advertiser conveys his message to the target segment. It is the medium by which an advertising message is communicated to the intended customers. All the tools that help an advertiser convey their message to the target segment together constitute media. Every approach accessible to the advertiser for communicating his message to the target segment is a part of the media. It includes channels of communication that facilitate the transmission of the advertiser’s message from the sender to the receiver.
Characteristics of Media
| Type of Media | Merits | Demerits |
| Television | Offers mass coverage, a high level of reach, the combined impact of sight, sound, and motion, prestige value, low cost per exposure, attention attraction, creativity, and impact. | It offers low selectivity, a short message lifespan, high production costs, creates advertising clutter, and leads to distrust and negative evaluations due to high ad clutter. |
| Radio |
Local coverage, lower cost, high frequency, focused segment selection, low production costs, broad reach, mass coverage, and the ability to examine ratings.
|
Only auditory creativity, noise, low attention-getting, short message lifespan, listener inattentiveness, scheduling and buying difficulties, and lack of visual elements. |
| Newspapers | Mass coverage, low cost, ample space, short lead time for ad placement, possible ad position choice, suitable for current ads, reader-controlled exposure, coupon insertion, affordability, flexibility, and timeliness. | Short advertisement lifespan, high ad clutter, low attention-getting, poor production quality, and selective exposure. |
| Magazines | Potential for focused segmentation, excellent production quality, message longevity, high information content, more readers per copy, high ad prestige, and reader involvement. | Extended lead time for ad placement, only visual, low frequency, lack of flexibility, limited reach and frequency, competition, and clutter. |
| Outdoor | Suitable for specific locations, high repetition, high visibility, geographic flexibility, ability to create awareness, comprehensive coverage of local markets, and high frequency. | Short exposure time, brief message, poor image quality, image problems, wear-out or clutter issues, limited message capabilities, and measurement problems. |
| Direct Advertising | High level of selectivity, reader-controlled exposure, high information content, opportunity for repeat exposures, personal touch, more profound impact, and measurability of results. | High cost per contact, often treated as junk mail, low reader interest, limited lifespan, high price, and requires specialized skills. |
| Internet | User-controlled, increased attention and involvement, message tailoring, information access, speed, low cost, updated ads, comprehensive customer contact, and high creativity. | There is potential for deception, privacy issues, limited production quality, poor reach, irritation, clumsiness due to repetition, and measurement problems. |
Related Articles:
- nature of business meaning
- nature of international business
- scope of international marketing
- determinants of economic development
- nature of capital budgeting
- nature of international marketing
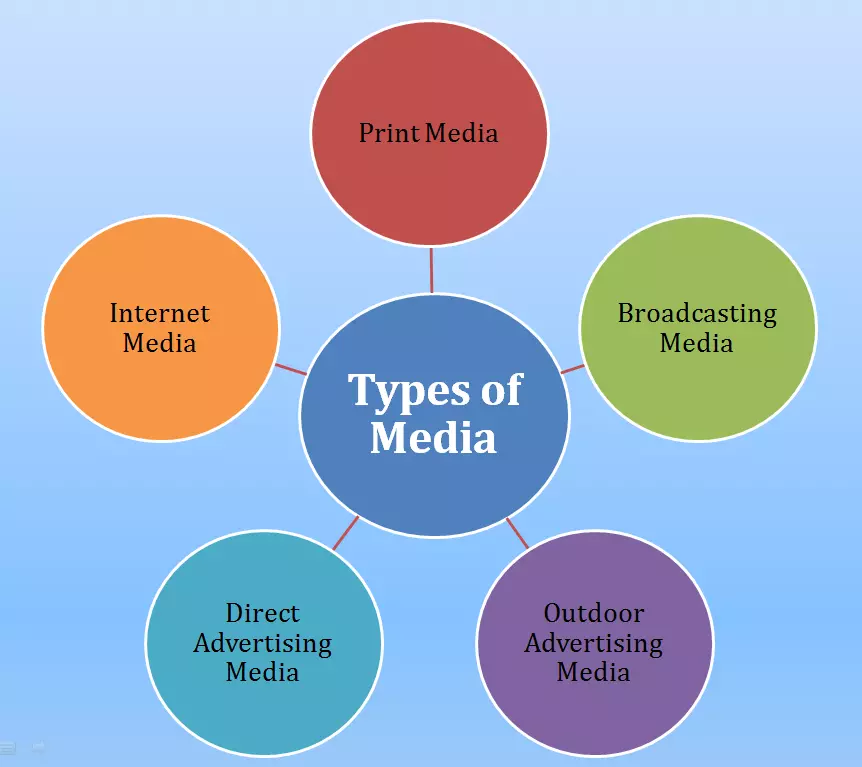
Types of Media
Advertisers wishing to create a huge effect at affordable budgets can select mass media for communicating their message as it is an ideal channel for them. The four vital mass media channels are newspapers and magazines. television, radio.
The significant factors of a media mix comprise the aforementioned channels or media classes because they are competent in improving the cost-effectiveness of the advertising campaign and they can reach a large number of the target segment. They are also capable of offering selectivity, believability and audio-visual attributes and, thus, are favoured by most advertisers. Direct advertising, window displays, outdoor, shop signs, etc.. are some of the other media used for advertising.
Advertising has different types of media alternatives to choose from, which can be categorized into the following groups:
1) Print Media
It refers to various materials or publications that are printed on paper and distributed. For example, Newspapers are either distributed by vendors or purchased by customers in their physical format. Unlike digital media, print media does not require any latest technology or excess funds. However, the growing popularity of mobile technology and the Internet which facilitates easy access to news and information from anywhere might decrease the role of print media in the future.
2) Broadcasting Media
Broadcast media, mainly television and radio, are usually associated with advertising. People who lack access to other sources of information or are unable to read and analyze current events often rely on these media for news and updates. Apart from news, broadcast media also provide valuable educational and entertainment content.
3) Outdoor Advertising Media
Outdoor Advertising Media is also known as out-of-home media or outdoor media. It is an influential tool that can be used in conjunction with the Internet, broadcast, and print advertising. This medium is used for reaching the target audience when they are outside of their homes, in public spaces such as billboards, bus shelters, transit vehicles, and digital screens. In today’s world, a successful advertising campaign cannot be achieved until and unless it has the support of outdoor media. This medium helps reach the target audience when they are outside of their homes. This medium is used in conjunction with the Internet, broadcast, and print advertising.
4) Direct Advertising Media
Direct Advertising Media is one of the oldest and most effective means of approaching the target audience. It is the most widespread form of means, which, instead of using an indirect medium like magazines or newspapers to deliver a message, uses all types of printed advertising that directly connects with the target audience. The printed form of material can be sent through the post, distributed to people who are passing along roadsides, distributed door-to-door, fixed under the wind-screen of automobiles, or distributed through retailers. When all this information written on the printed matter is sent directly through the mail, then it is known as direct mail advertising.
5) Internet Media
Many major changes have been witnessed in the behaviour of the consumer and their buying decisions owing to the Internet age that gained widespread and rapid popularity in the last ten years. This change has led to the emergence of a new kind of customer who is well-informed and capable of doing immense research work before making a buying decision. These new customers spend a lot of time on the Internet, which can be for professional and/or personal motives. Thus, these customers can be the new target audience for marketers who use internet platforms to interact and reach out to them.
Role of Media in Disaster Management
The media plays an important role in disaster management. In this context, it performs the major functions mentioned below:
i) Media help in policy formulation by conducting public debate surveys or polls.
ii) Surveillance of the environment, which means the collection and distribution of information concerning events in the climate/environment. Several climatic information is potentially related to natural disasters, which can be communicated regularly and more frequently at the time of disaster. The best example is a cyclone, Media can play a very important role in the dissemination of information such as the formation of depression on the sea, its movement towards the coast, areas likely to be affected, etc.
iii) Disaster Awareness Education to the masses can be given by the media. Today we have about 50% illiterate people in India but most of them do have access to radio or television.
iv) Long-term preparedness and mitigation strategies can be explained effectively to the masses through various media.
Why Media Covers Disaster News?
This is because disasters are unusual, sudden events which cause enormous loss of lives and property. It brings many dramatic and traumatic stories. It depends on how the journalists deliver the news. Most of the time, they try to find fault in providing relief to the victims and highlighting the impact on the affected community. Sometimes, this news encourages international fundraising and creates more public sympathy for the affected people. The amount, depth, and period of coverage will depend on the scale and frequency of the disaster, the speed with which the information can be obtained, and the amount of public interest in the subject. The media strongly impact the perception of and response to disasters. This role of media in a disaster is multipurpose and can be broadly classified into three categories:
- Informative
- Suggestive
- Analytical
Relationship between Media and Society
Media institutions are a part of society. The news media ought to be free and fair because of its watchdog function. The news media is expected to watch the government, businesses and other institutions closely. It is expected to bring issues into the public domain for debate and discussion. Therefore, It is incumbent on the government to not only protect the autonomy of the press but also ensure a free and fair distribution of news to the public. This is to ensure that people who depend on information provided by media remain updated and connected to the world. The media is expected to share news without fear or favour and help articulate public opinion on issues that concern them. Media functions as a conduit between the public and the powers that be.
FAQ
1. What is media?
Media refers to the communication channels through which we share or gather information. It can be done through newspapers and magazines, television, radio, billboards, education, telephone, Internet, marketing, fax, advertisement, and billboards. According to Wikipedia ” media are the outlets or tools used to store and deliver content; semantic information or subject matter of which the media contains”.
You May Also Like:-
