Table of Contents:-
- Meaning of Human Resource Information System
- Definition of Human Resource Information System
- Need for human resource information system
- Objectives of human resource information system
- Components of human resource information system
Meaning of Human Resource Information System
A human resource information system is a systematic procedure for collecting, storing, maintaining, and retrieving data needed by an organization about its human resources and various activities that are relevant to its management in an accessible and central location. An HRIS (Human Resource Information System) comprises a database that stores relevant data, organized in one or more files, and a database management system, which provides how users of the system access and utilise these data.
The HRIS includes features that enable users to input new data and modify existing information. These programs provide users with the option to select pre-defined reports that are printable or viewable on a monitor. Reports may address any of several different HRM issues, (e.g., succession planning, compensation planning, and equal employment opportunity monitoring). HRIS also generally include tools by which users or system administrators may generate ad hoc reports and select specific cases or subsets of display cases. HRIS data is highly valuable in the field of Human Resource Planning (HRP), enabling the use of statistical tools for the development of appropriate models and the optimization of human resource demands.
Definition of Human Resource Information System
According to Boyett et al, “The main intent of Human Resource Information System (HRIS) is to keep an accurate, complete, updated database that can be used when needed for reports, recordkeeping, and automating routines and tasks such as application tracking”.
According to Walker, “HRIS is a systematic procedure for collecting, storing, maintaining, and retrieving, and validating data needed by an organisation about its human resources, personnel activities, and organisation unit characteristics”.
Need for human resource information system
Various problems in manual record-keeping are the main reasons which led to the emergence of human resource information system
1) The Clerical Work Involved is Quite Labour-Intensive and Costly
When kept manually, personnel records do not offer up-to-date information at short notice. It is difficult to make entries on forms and ret continuously and keep pace with ongoing changes daily.
2) More Susceptible to Error
Manually transferring data from one record to another can increase the risk of errors. Wrongly transferring data to documents can lead to the duplication of entries, and this often happens because of confusion.
3) Disorganised Arrangement of Information
The decentralization of information, with records handled by different individuals in various departments and stored separately, makes it inaccessible from a central location.
4) Manual Analysis of Data is Time-Consuming
The manual data analysis is time-consuming and often not readily available for decision making. The manual systems must offer reliable, accurate data at short notice when the organisation grows.
5) Maintaining Manual Records is Difficult
To conduct personnel research personnel audit, and human resource accounting, the personnel manager requires lots of data relating to employees working in the organisation. Workforce planning activity, too, needs a significant amount of data. Modern business organizations find the manual records system lacking and inadequate in meeting their information requirements. In other words, the fundamental need for a human resource information system arises from the challenges in maintaining and the limitations of manual records systems.
Related Articles:
- nature of business meaning
- nature of international business
- scope of international marketing
- determinants of economic development
- nature of capital budgeting
- nature of international marketing
Objectives of human resource information system
Objectives of HRIS are as follows:
1) To create an HR information hub for the whole organisation, which facilitates effective people-to-people and people-to-information contacts.
2) To enhance the ability of human resource management to leverage and absorb new and emerging challenges and opportunities of organisational behaviour.
3) To ensure efficient data collection, storage, and distribution of HR-related information in a paperless work environment.
4) To facilitate faster processing of information and more effective decision making to make the optimum use of the available human resources.
5) To enable the HR managers to devote more time to strategic issues by relieving them from routine operations through the Employee Self-Service Systems (ESS). The ESS in the HRIS lets the employees have direct access to select information regarding training, payroll, and other relevant matters without disturbing the HR manager.
6) To provide support for future planning and also for policy formulations, both at macro and micro levels. At the enterprise or micro level, HRIS forms the basis for human resource management and more particularly HRP.
7) To establish an integrated system for achieving an efficient and purposeful integration of various human resource functions and effective deployment of strategic human resources.
8) To provide required inputs to enterprise-wide strategic decisions, like redundancy, rightsizing, competency profiling, change of technology, etc.
9) To maximise the accuracy, reliability and validity of workforce records, and eliminate the cost and wastages associated with the manual maintenance of HR records.
10) To facilitate monitoring of human resources demand and supply in balances and evaluation of the policy on the development and utilisation of human resources.
Components of human resource information system
Components of the human resource information system and their working are shown in the image:
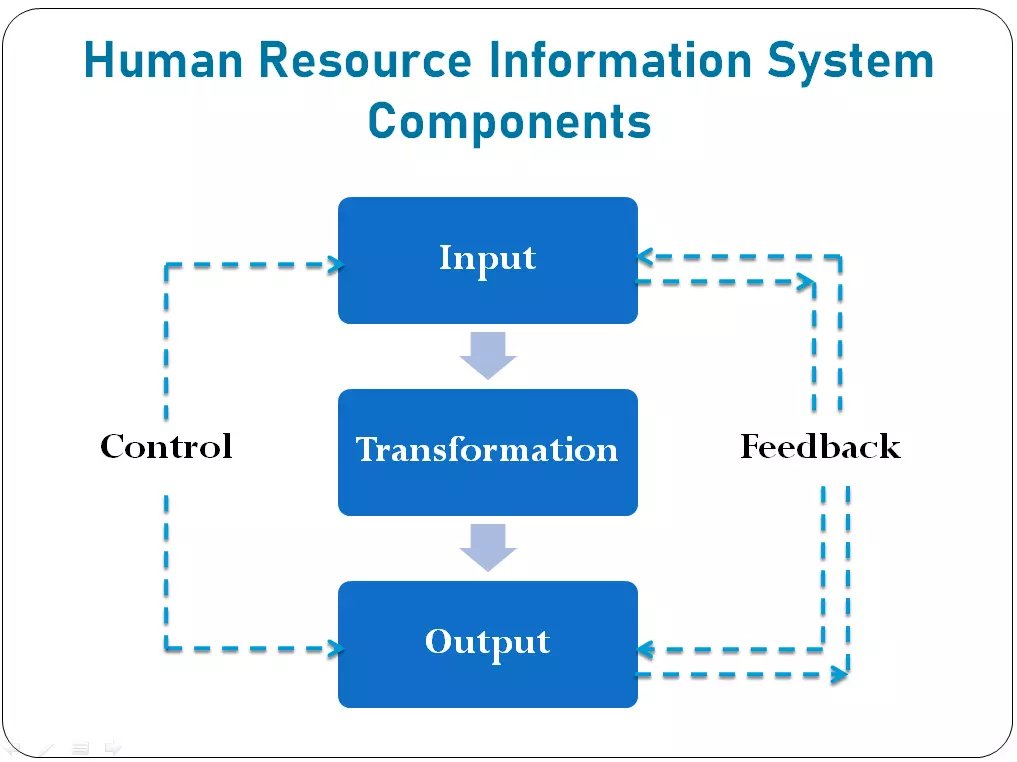
1) Input
The inputs of the system normally consist of employee information, company policies and procedures and other personnel-related information that is entered into the system to be used. This function provides the capabilities needed to get the human resource information into HRIS. The establishment of procedures and processes for gathering essential data is a fundamental step. In simpler terms, who, when, and how will collect the data? It’s essential to code the collected data before entering it into the system. After capturing the data, it is essential to validate it to ensure its accuracy. Using validation tables, one can determine if the data meets the criteria for acceptability. The system should be able to easily update and modify the validation table.
2) Transformation
The transformation portion of the system is associated with the actual computer It usually includes software or written instructions that tell the computer what to do, how to do it and when to do it. This function is responsible for the actual updating of the data stored in the storage devices. If changes occur in human resource information, they should be incorporated into the system. It is often advantageous to retain the old data for historical reference as new data becomes a part of the system.
3) Output
The output of the system is the actual use of the newly processed material. For example, this could entail the production of a report regarding the age and gender distribution of employees within the company. This aspect of an HRIS is the most recognizable because most HRIS users are not responsible for collecting, editing, validating, and updating data. Instead, they focus on the information and reports generated by the system. Most human resource reports consist of selecting a segment of the total population for further evaluation, performing some type of calculations, using the population and providing a report containing specific information about the selected population and the calculation of results. The requirements placed on the output function are the primary factors that determine the specific type of software to be utilized.
