Table of Contents:-
-
- Meaning of Human Resource Accounting
- Definition of Human Resource Accounting
-
Define Human Resource Accounting
- Nature of Human Resource Accounting
- Objectives of Human Resource Accounting
- Process of Human Resource Accounting
Meaning of Human Resource Accounting
Human Resource Accounting (HRA) may be considered an accounting system which recognises human resources as an asset and records it in the books of account after measuring its value in the same way as other physical resources. Such accounting may generate and present valuable and important information related to human resources.
Definition of Human Resource Accounting
According to Stephen Knauf, “Human resource accounting is the measurement and quantification of human organisational inputs such as recruitment, training experience and commitment”.
According to R. L. Woodruff, “Human resource accounting is an attempt to identify and report investment in human resources of an organization that are presently not accounted for in conventional accounting practice”.
Define Human Resource Accounting
As per Flamholtz, “Human resource accounting is the measurement of costs and value of the people for the organisation”.
According to the American Accounting Association Committee, “Human resource accounting is the proper identification and measuring data about human resource, and communicating this information to interested parties”.
Nature of Human Resource Accounting
The provided information presents the nature of human resource accounting as follows:
1) It involves recording the valuation of human resources in the books of accounts. The organization also keeps a record of changes in human resources over time.
2) It involves disclosure of the information in the financial statements of an organisation for communication.
3) It involves the measurement of the cost and value of human resources.
4) In this accounting system, the identification of human resources is a key component. The organization includes all categories of employees, from top management to the bottom, in its human resources.
Related Articles:
Objectives of Human Resource Accounting
Objectives of human resource accounting are given as follows:
1) To facilitate the preparation of the human cost or budget for performing human resource functions like acquisition, development, and compensation of employees.
2) To help the management in monitoring the utility of human resources constantly to achieve the optimum utilisation of labour.
3) To serve as a basis for decisions concerning the human resources of the organisation.
4) To provide methods and standards for evaluating the worth of people to the organisation effectively.
5) To provide quantitative information about the cost and value of human resources available within the organisation.
6) To permit all the stakeholders of the business to have a fair knowledge of the value of the existing human resources.
7) To carry out planned and measured changes in the value of the human resources of an organisation.
8) To provide an early warning to the management about the impending changes in the value of human resources. This should enable the organisation to act adequately and appropriately to conserve its precious human resources.
9) To enable the organisation to reward the employees based on assessing their values.
10) To help in the development of managerial principles and practices by clarifying the financial effects of various practices.
11) To encourage the managers to have human resource perspectives in all decisions by sharing numerical information about human resources.
Process of Human Resource Accounting
The process of designing and implementing HR accounting involves the following steps:
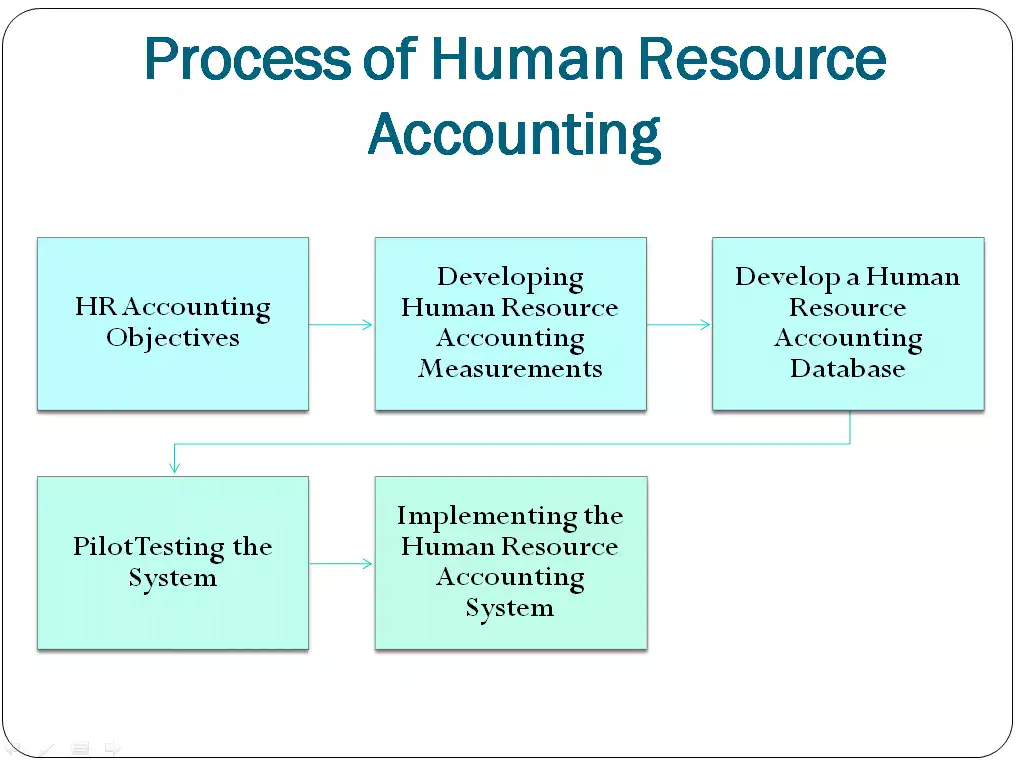
Step 1: HR Accounting Objectives
The objectives of the human resource accounting system should stem from the management’s requirements for human resource information. It is necessary to define these requirements explicitly. As a part of the detailed study and analysis of the organisation’s human resource management process, each organisational unit responsible for human resource management should define its functions; and indicate the kinds of decisions made, their relative frequency and the information needed to make those decisions.
The analysis of these information requirements about the current information flow and the specification of new information are necessary. After completing this analysis, we can define the basis of the human resource accounting system regarding its scope and objectives. The objective may be a total HRA system, a problem-oriented system, a partial system such as a budgeting system for human resource costs, or setting standard costs.
Step 2: Developing Human Resource Accounting Measurements
The second step is to select the types of HRA measurements desired. It is essential to decide between:
1) Single measurement or a set of measurements; and
2) Monetary or non-monetary measurements and measurements of costs or value, or both. In the next step, we must ensure the validity and reliability of the chosen measurements before converting them into usable forms.
Step 3: Develop a Human Resource Accounting Database
The inputs required for Human Resource Accounting constitute the database. These include psychological measurements, cost data, timesheets, etc. In typical cases, it will become necessary to restructure the organisation’s accounting classification to ensure that all personnel-related costs are classified separately.
Otherwise, these cost elements are buried and covered in one single classification administration and general expenses. The accounting classification must centre around responsibility areas like recruitment, training, and management development.
In addition to re-structuring the accounting classification, the database must also include non-financial information such as employee attitude survey feedback as a standard ongoing basis. Similarly, it’s important to consider the probabilistic estimates of employee mobility, which are compiled during the human resource planning process when measuring the value of human resources.
Step 4: Pilot Testing the System
After the objectives have been defined, measurements developed, and the necessary database is made available, the next step is to pilot-test the system. Care should be taken that the test is not influenced by extraneous problems and that the management’s support and cooperation are available throughout the processes of design and development of the system.
Step 5: Implementing Human Resource Accounting System
The final phase is the implementation process. This process essentially includes standardizing input-output documents, forms, and similar elements while acquainting the staff with the new system. Staff orientation as to the uses, purposes, and methods is a key activity to operationalise the Human Resource Accounting system without much hassle.
Any system, over some time, may become out of step either because of inherent constraints or changes in management needs. A continuing review would make the system more responsive to the changing needs, and modifications required would be easy to carry out either by simple adjustments in the existing system or by following the design and implementation process if there is a need for the same.
FAQ
1. What is HR Accounting?
According to Flamholtz and Lace (1981), “HR accounting may be defined as the measurement and reporting of the cost and value of people as organisational resources. It involves accounting for investment in people and their replacement costs, as well as accounting for the economic values of people in an organisation”.
2. What is the need of hra?
HRA is a method that organisations use to assign a financial value to their human resources and measure and manage human capital to align them with organisational goals and objectives.
3. What are the various features of human resource accounting ?
