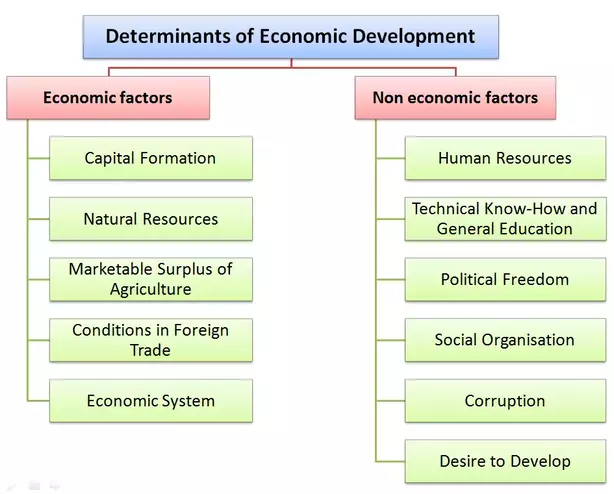
Determinants of Economic Development
There are mainly two types of determinants (factors) that affect the economic development of a country.
- Economic factors
- Non economic factors
These factors are as follows:
Related Articles:
- nature of business meaning
- nature of international business
- scope of international marketing
- nature of capital budgeting
- nature of international marketing
1) Economic Factors in Economic Development
Economic factors include all aspects of the economy that impact the growth and progress of a country, including international trade, fiscal policy and monetary policy, industrialization, and infrastructure development. Other important economic factors include access to credit facilities, availability of skilled manpower, low inflation rates, etc. However, it’s not just these particular factors; it’s how they work together that determines whether a country can develop economically or not.
It is crucial to analyze the impact of certain factors on economic development, including but not limited to the following:
i) Capital Formation
Capital formation refers to the process of making new assets and investments that can generate income and profit over time. Investment in capital formation is important for economic development as it includes investing in new types of equipment, building infrastructures, or obtaining funds for research and development projects. It is now widely accepted that a country seeking to accelerate the pace of growth must save a high ratio of its income to increase investment. Relying heavily on foreign aid is a risky proposition and should be avoided. Increasing the amount of capital available will lead to improving the productivity and competitiveness of a country. However, capital formation requires considerable savings, which can be very challenging for many developing and underdeveloped countries.
ii) Natural Resources
The availability of natural resources is an important factor that influences the development of an economy. These resources include land area, the quality of the soil, forest wealth, river systems, minerals, oil, favourable climate, etc. The abundance of natural resources in a country is essential for economic growth. Therefore, countries that are rich in natural resources have a significant advantage over those countries which are not flourished with these resources.
The importance of natural resources cannot be overstated because a country deficient in natural resources will struggle to develop rapidly. Natural resources serve as the basic building blocks for industries to manufacture goods and provide services. For example, Minerals are used in the production of electronics, while oil serves as the primary source of energy for transportation. Forests provide wood for construction and paper production, while fertile soil is necessary for agriculture. A favourable climate is also necessary for agriculture, as it affects crop yields and livestock production.
iii) Marketable Surplus of Agriculture
Improving the agricultural production of a country will lead to greater output and economic growth. Countries must prioritize these factors to meet the demands of a growing population and ensure food security. By adopting advanced technology, modern farming techniques, and efficient supply chains, countries can boost their agricultural sector and reap the benefits of a thriving economy.
iv) Foreign Trade
Foreign trade and the exchange of goods or services between countries are affected by many factors such as political stability, economic policies, foreign trade relations, natural disasters, climate change, fluctuating currency values and interest rates affecting the profitability of businesses. Tariffs and other trade barriers that are enforced by countries to protect their economies impact foreign trade conditions. If a country exports more goods and services than it imports will result in a surplus of money and a greater potential for economic development in that country. Therefore, countries should focus on improving their balance and terms of trade to achieve economic development. Today’s world technological advancements such as the Internet have contributed greatly to the growth and expansion of global markets and foreign trade. It has revolutionized the way businesses operate, by making them reach their customers from all corners of the world.
v) Economic System
The economic system and historical context of a country play an important role in determining its development prospects. It is important to understand that economic systems are not designed similarly to each other. A country’s economic system can either facilitate or hinder its development. It is important for countries to carefully consider their economic system and historical context when planning for economic development. By doing so, they can create an environment that fosters growth and attracts foreign investment, which will lead to a prosperous future.
2) Non-Economic Factors in Economic Development
The development of a society is not solely dependent on economic factors but also on Non-economic factors. Non-economic factors are as much important in the development of a country as economic factors are. Non-economic factors must be considered along with economic factors. While making decisions about investment priorities and policy interventions related to improving economic outcomes as culture, social norms, political stability, and environmental conditions are also significant determinants of economic growth.
Here we attempt to explain how these factors influence the process of economic development:
i) Human resources
Human resources are an essential factor in the economic development of a country. By investing in education, training, and healthcare, and reducing superstitions, countries can improve the overall health, skills, productivity and well-being of the employees, leading to sustainable economic development. Human resources provide the necessary labour power for production, and in countries where the workforce is efficient and skilled, the capacity to contribute to growth is very high. On the other hand, the productivity of the unskilled, illiterate, disease-ridden, and superstitious workforce is generally low, and they do not offer much hope for developmental work in a country. Therefore, It is important to invest in education and training programs to improve the skills and knowledge of the workforce. This will increase productivity and create a more competitive and innovative environment for the workforce to work in.
ii) Technical Know-How and General Education
Technical know-how and general education go hand in hand when it comes to achieving success in the modern world. It is widely acknowledged that the level of technical know-how directly impacts the pace of development. As scientific and technological knowledge continues to advance, people are discovering increasingly sophisticated techniques of production that steadily enhance productivity levels. Technology has reached a level of sophistication but still, a strong emphasis is given to the importance of research and development to continue advancing.
iii) Political Freedom
Political freedom is a vital component of an equitable society. Every country’s ability to progress and prosper is largely dependent on the level of political freedom it enjoys. It is the ability to participate in the political process of a society without the fear of persecution or punishment. It cannot be achieved in isolation from other factors, such as economic development and historical legacies of exploitation. By taking a holistic approach to these issues, we can work towards a more equitable and just world for all. When businesses are granted the freedom to share their resources and participate in import and export, are more likely to contribute to the development of their country. It fosters an environment of innovation and creativity, which is important for economic development.
iv) Social Organisation
It refers to the patterns of relationships and groupings that people form to meet their needs, such as food, shelter, safety or friendship. Mass participation in development programs is important for accelerating the growth process. However, people show interest in the development activity only when they feel that the benefits of development will be fairly distributed. Experiences from different countries have shown that when a social organization is flawed, elite groups tend to monopolize the benefits of growth, and the general mass of people develops apathy towards the country’s development programs. Under the circumstances, it is futile to expect that the people will participate in the development projects undertaken by the country.
v) Corruption
Corruption is a rampant issue in developing countries, affecting various levels of society and hindering their growth process. If it is left unchecked, it will let capitalists, traders, and other economic classes exploit national resources for their interests. The regulatory system is also often misused and the licenses are not always granted based on merit.
vi) Desire to Develop
The rate of economic development of a country heavily depends on people’s collective desire to progress. If a country’s people lack awareness and have accepted poverty as its fate, then there will be little hope for development. For economic development people and communities alike must aspire for progress and strive towards a brighter future.
Impact of Economic Environment on International Business
1) Extent of liberalisation, globalization, and integration with the global economy.
2) Economic indicators of the local economy in present times and what they are expected to be short.
3) Degree of competitiveness in a particular field.
4) Supply situation of a particular product or service at a particular time.
5) Situation concerning the factors affecting the pricing of products and services.
6) Demand dynamics for a particular product in a given market.
7) Likelihood of short-term and long-term profitability because of multifarious factors.
8) Depression or resurgence of economies that result in the rise or decline or stability in economic growth rates at global and national levels.
9) Extent of regulation and management of national economies and financial sector by the government.
10) Availability of foreign investment in the form of FDI and FII.
11) Rate of inflation in an economy.
12) World food production levels at a certain time.
13) The current state of the global economy and what is likely to be short.
You May Also Like:-
